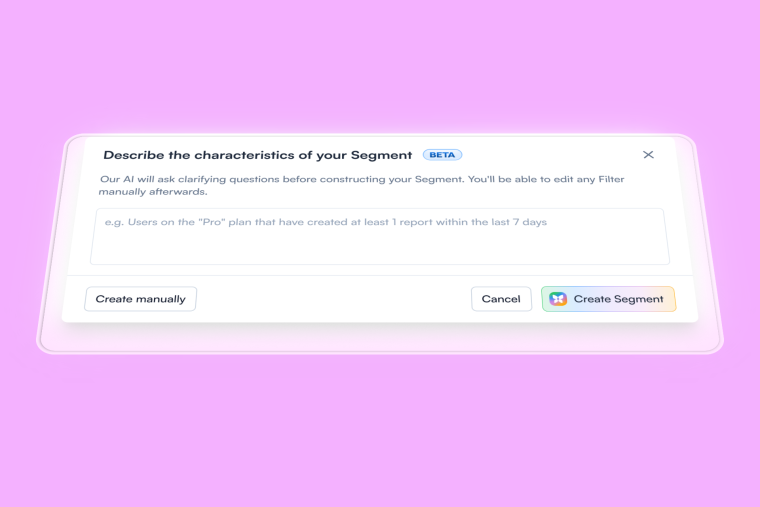
Onboarding is where your product meets its users—and where they decide whether to stay. A great onboarding strategy is a guided tour showing users exactly how your product solves their problems while making them feel like they’re a natural pro at using it, which can significantly enhance user retention.
Segmenting users based on user type to create personalized onboarding experiences is essential. Different user types may have unique needs and interactions with the product, which can be effectively addressed by contextual onboarding strategies and behavioral analytics.
If you’re building your first strategy, the choices can feel endless. Should you roll out tutorials? Highlight features? Throw in some celebratory confetti for milestones? The secret lies in creating a journey that’s as functional as it is delightful And, it’s a fine line to find.
Designing onboarding processes that are engaging, easy to understand, and relevant to users is crucial for creating a memorable user experience. Implement user onboarding to create engaging and effective experiences for new users.
This guide will take you through the essentials of creating a user onboarding strategy that works—practical steps, proven principles, and everything on that line.
Introduction to user onboarding
Onboarding is a critical component of a product’s overall user experience. It is the process of guiding new users to quickly unlock value with a product or service. The goal of onboarding is to reduce the time to value and help new users reach the “Aha moment” where they understand why they need the product. In this section, we will explore the definition and importance of onboarding, as well as the key elements of an effective onboarding process.
It's the process of making new users feel comfortable and confident when using a product. It is crucial for new users to become successful when adopting a product, and the likelihood that new users become successful is directly related to the quality of the onboarding process. A well-designed onboarding process can increase user engagement and retention, and is a key factor in determining the overall success of a product.
“User onboarding is the process of increasing the likelihood that new users become successful when adopting your product.”
What is user onboarding?
User onboarding is the process of guiding new users to their first success with your product. New user onboarding highlights key features, simplifies complex steps, and helps users achieve their goals quickly by enhancing user experiences through effective onboarding strategies. Considering the user's perspective, effective onboarding should be intuitive and engaging, addressing the specific needs and preferences of users to enhance retention and overall satisfaction with the product. New users who experience personalized onboarding are 30% more engaged than those who undergo generic onboarding.
A great onboarding strategy ensures users feel confident and supported from the start, making it easier for them to see the value your product offers.
User onboarding is the process of increasing the likelihood that new users become successful when adopting your product.
Why is user onboarding important?
User onboarding is crucial for radically increasing the likelihood of user success—it’s the foundation for engagement, retention, and long-term success.
Keeps users hooked from day one: Onboarding walks new users through your product, showing them exactly how it solves their problems. First impressions count! Use in-app guides and instructional videos to walk users through essential tasks, ensuring they quickly understand how to use the platform effectively.
Cuts down on churn: Confused users quit. Onboarding clears the confusion, giving users a reason to stay and explore.
Fast-tracks their “aha!” moment: Help users connect the dots between their goals and your product’s value—and fast. The sooner they get it, the sooner they’ll love it.
Makes your product easier to adopt: Good onboarding simplifies even the most feature-packed tool, making users feel like pros from the start.
Turns users into advocates: Satisfied users stick around, share your product with others, and maybe even leave that five-star review you’ve been hoping for.
Understanding New Users
New users are individuals who have recently signed up for your product or service and are just beginning their journey with it. Understanding their needs and pain points is crucial for creating an effective user onboarding process. Segmenting users based on user type can help tailor the onboarding experience to better address their unique needs and interactions with the product.
Typically, new users have a limited understanding of your product’s features and functionality, and they may struggle to navigate the user interface. They often have specific goals and objectives they want to achieve, such as completing a task or solving a problem. By recognizing these challenges, you can design an onboarding process that addresses their needs and helps them quickly realize the value of your product.
New User Needs and Pain Points
New users have several needs and pain points that must be addressed during the onboarding process. These include:
Clear Value Proposition: New users need to understand how your product can help them achieve their goals. Clearly communicate the benefits and value your product offers right from the start.
Easy Access to Features: Ensure that key features and functionalities are easily accessible. Avoid overwhelming new users with too many options at once; instead, guide them to the most important features first.
Intuitive Navigation: Simplify the user interface to make navigation straightforward. Use clear labels, logical layouts, and intuitive design to help users find what they need without frustration.
Minimal Cognitive Load: Reduce complexity by breaking down tasks into manageable steps. Avoid information overload and provide just enough guidance to help users progress.
Opportunities for Feedback and Support: Offer channels for users to ask questions, collect feedback, and seek help. This could include in-app support, FAQs, or a dedicated customer support team.
Sense of Progress and Accomplishment: Use progress bars, milestones, and celebratory messages to give users a sense of achievement as they complete tasks. This helps keep them motivated and engaged.
User's Specific Needs: Address the user's specific needs and preferences by creating an intuitive and engaging onboarding process. This enhances retention and overall satisfaction with the product.
By understanding these needs and pain points, product teams can design an onboarding process that is tailored to the needs of new users, helping them become successful and engaged users.
How to create a stellar onboarding strategy in 5 steps
You want to guide users without overwhelming them. Give too much information, and they check out. Too little, and they’re left guessing. Effectively implementing user onboarding strategies is crucial to strike this balance. Let’s look at five actionable steps to help build an onboarding strategy that informs and engages without losing their attention. User onboarding involves three stages: Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary onboarding.
Segmenting users based on user type can create a more effective onboarding strategy. Different user types may have unique needs and interactions with the product, which can be effectively addressed by contextual onboarding strategies and behavioral analytics.
Understanding user journeys is essential to identify barriers that may hinder users from reaching important milestones, such as their ‘aha!’ moment. By comprehensively analyzing these journeys through user feedback and data collection, businesses can improve the onboarding process and enhance user experience, ultimately leading to quicker adoption and satisfaction. This approach helps to improve user onboarding by identifying and addressing weaknesses in the process.
1. Decide who’s responsible
Do not let the responsibility for user onboarding fall through the cracks. Without ownership and consideration of the user's perspective, your product’s onboarding will be an uninspired afterthought.
Teams assign accountability depending on their size and maturity. For early-stage startups, it might be one of the founders. For mid-stage teams, it could be a product manager, marketing team member, customer success rep, designer, or someone else. Later-stage teams may have a dedicated team.
Account managers can also play a vital role in facilitating active onboarding processes. They guide new users through product usage, addressing their questions to ensure successful product adoption and enhancing the onboarding experience, which can vary from one-on-one sessions to group interactions.
A marketing manager can play a crucial role in personalizing onboarding experiences by identifying user roles and tailoring the process to meet the unique needs and goals of each segment, such as tracking campaign performance.
Ideally, the same person or team works on all aspects of onboarding. This includes the first experience after signup and for new features or redesigns etc. This will ensure a consistent experience for users and better alignment with company objectives.
🤔 Which teams use Chameleon the most?
Data from a previous Chameleon Benchmark Report shows that the teams using Chameleon to build onboarding flows like product tours the most are:
✅ Product management
✅ Product marketing
✅ Engineers
✅ Customer Support
2. Understand user behavior
User behavior doesn’t just happen—it’s the result of motivation, ability, and triggers working together. BJ Fogg’s behavior model explains this perfectly:
Motivation drives the user to achieve a goal
Ability ensures they have the tools and knowledge to take action
Triggers prompt them to act at the right moment

User behavior doesn’t just happen—it’s the result of motivation, ability, and triggers working together. BJ Fogg’s behavior model explains this perfectly:
Motivation drives the user to achieve a goal
Ability ensures they have the tools and knowledge to take action
Triggers prompt them to act at the right moment

Mapping the user journey in onboarding means understanding how these elements interact at each step. It is crucial to walk users through the onboarding process by providing in-app guides and instructional videos that help them quickly understand essential tasks.
Start by identifying what motivates your users. Is it solving a specific problem? Exploring new features?
Next, ensure they can act—clear instructions, intuitive navigation, and the right resources are key.
It’s also important to cater to different learning styles by including various content formats, such as video tutorials and support documentation, to enhance user experience and adoption.
Finally, use triggers like prompts or notifications to guide them and identify areas where users struggle.
For example, if your onboarding goal is to get users to upload their first file:
Motivation: Highlight the benefits of having their files organized in one place.
Ability: Provide a one-click upload button with clear instructions.
Trigger: Use an in-app prompt like “Start uploading your files now!”
3. Figure out your “aha” moment
Getting to “aha” should be the goal of your user onboarding. This applies to both product onboarding and also feature or redesign onboarding.
The “aha” moment is the time when a user internalizes the value your product provides. It’s when they are ready to buy (if on a free trial) or deepen their relationship with the product (become a product ambassador/share with friends/give access to more data/etc.)
Tracking custom user events can significantly enhance the onboarding process. Businesses can optimize their strategies and improve user retention by analyzing user behavior and identifying key moments of engagement, such as the ‘aha!’ moment. A high month 1 retention rate indicates that users find value in the product early on, suggesting successful onboarding.
If you’re not sure what your “aha” moment is, start with a hypothesis. Ask yourself:
What’s the core benefit of your product?
Which feature do users love most?
What excites your most loyal users?
Test your hypothesis with surveys or user interviews to validate it. Once identified, map out the steps users need to take to reach this moment from the user's perspective. Then, refine the process by asking:
Is the path clear? Are unnecessary steps causing drop-offs? What’s the shortest route to that “aha”?
Do users know what to do next? Are the directions obvious? Do users have the motivation, ability, and triggers to move forward?
Answering these questions ensures two things. First, your product design removes barriers to success. Second, your onboarding flow actively guides users to their “aha” moment with clarity and purpose by helping them complete key tasks.
4. Use a combination of channels
Effective onboarding doesn’t rely on a single channel—it uses a mix of tools to motivate, educate, and engage users. The three most common channels are emails, in-app messages, and product tours.
Emails are your follow-up champions. Use them for transactional updates (like signup confirmations) or to bring inactive users back into the fold. But remember, they’re out of context—users might read them anywhere. Stick to motivating them with benefits, not a laundry list of features.
In-app messages hit users right where it matters—inside your product. These are perfect for introducing new features, sharing tips, or giving updates while users are already engaged. Keep them short, clear, and relevant to spark curiosity and exploration.
Product tours are like a guided walk-through of your product’s highlights. With well-placed tooltips or hotspots, you can nudge users toward key actions without overwhelming them. Focus on what helps them succeed, not what looks good for you.
 Monika, VP Marketing at Zuora, recounts: “We’ve been trying multiple channels, including email and webinars, but they don’t provide the value that product tours do.”
Monika, VP Marketing at Zuora, recounts: “We’ve been trying multiple channels, including email and webinars, but they don’t provide the value that product tours do.”
This may require coordination between teams in your organisation. You could set up a regular “user education” meeting or group to build greater coherence. Start by setting out clear objectives for each channel; what is the goal and how does it relate to new user activation.

5. Analyze and iterate quickly
User onboarding isn’t a one-and-done task—it’s an ongoing process. If you’re waiting six months to revisit it, you’re already falling behind.
Start by defining what success looks like. Do you want users to complete a specific action, reach their “aha” moment, or engage with a key feature? Once you have clear goals, map your user onboarding flow. Identify the moments where users need help, motivation, or direction.
Onboarding checklists can be particularly useful here, as they guide users through essential tasks and utilize psychological principles to keep them engaged. But don’t let perfection hold you back. Build a simple first version and launch it. Then, analyze the results from the user's perspective—where do users hesitate? Where do they drop off? Use data, feedback, and user behavior to fine-tune your process.
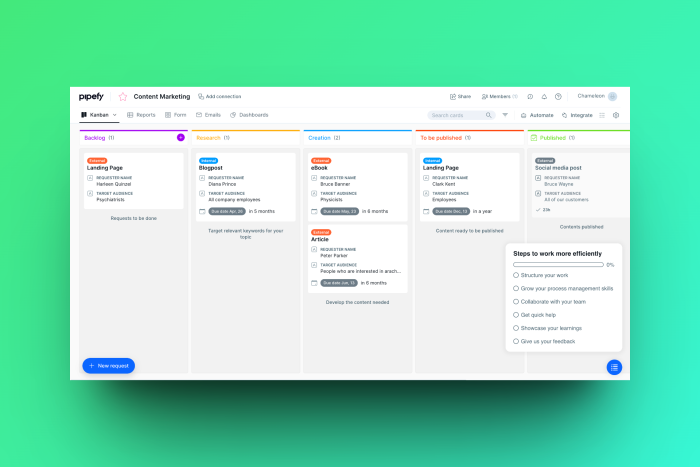
Understanding the onboarding process in-app
The onboarding process is the series of steps that new users take as they learn about and begin using a product. This process typically includes a combination of interactive tutorials, guided tours, and in-app messages. The onboarding process should be designed to be intuitive and easy to follow, with clear instructions and minimal confusion. By streamlining the onboarding process, product teams can reduce the likelihood that new users will become frustrated or disengage, radically increasing the likelihood that they will find value in the product quickly.
It is key to walk users through essential tasks using in-app guides and instructional videos to ensure they quickly understand how to use the platform effectively.
Guide users through configuration.
One of the key steps in the onboarding process is guiding users through configuration. This involves providing users with the information and resources they need to set up and customize the product to meet their individual needs. Considering the user's perspective is crucial here, as effective onboarding should be intuitive and engaging, addressing the specific needs and preferences of users. Configuration tasks can include setting up account information, customizing dashboards, and integrating with other tools and services. By providing clear guidance and support during the configuration process, product teams can help users get up and running quickly and easily, ensuring a smooth start to their journey with the product.
Assisting with setup and payout activities
Facilitating setup and payoff tasks is a critical component of the onboarding process. From the user's perspective, setup tasks refer to the steps that users must take to configure and customize the product, such as setting up account information and integrating with other tools and services. Payoff tasks are the actions that users take to achieve their goals and realize the value of the product, such as completing tasks and achieving milestones.
By providing clear guidance and support during both setup and payoff tasks, product teams can help users get up and running quickly and easily, reducing the likelihood that they will become frustrated or disengage. This approach ensures that users can see the product's value early on, leading to higher engagement and retention rates.
Onboarding checklists
Onboarding checklists are a useful tool for ensuring that new users complete all the necessary tasks to get started with a product. These checklists can include items such as setting up an account, completing a tutorial, or contacting customer support. By providing a clear and concise checklist, products can help new users stay on track and ensure that they have a positive onboarding experience.
Mobile app user onboarding
Mobile app onboarding refers to the process of guiding new users through the initial stages of using a mobile app. This process is critical for ensuring that users understand how to use the app and can achieve their goals. It is essential to walk users through the onboarding process using in-app guides and instructional videos to help them quickly acclimate to the software. Given the unique constraints and opportunities of mobile platforms, a well-designed mobile app onboarding process can significantly enhance user engagement and retention. A comprehensive resource center can further support this by providing various self-service support materials, enabling users to independently find solutions to their questions.
Approaches for effective mobile user onboarding
Creating a successful mobile app onboarding process involves several key strategies:
Interactive Tutorials and Guided Tours: Use interactive tutorials and guided tours to introduce users to key features and functionality. These tools can help users quickly understand how to navigate the app and use its core features.
Clear and Concise Instructions: Provide clear and concise instructions to help users complete tasks. Avoid lengthy explanations and focus on actionable steps that guide users through the process.
Opportunities for Practice: Allow users to practice and reinforce their learning. Interactive elements, such as quizzes or mini-tasks, can help users become more comfortable with the app.
Analytics and User Feedback: Use analytics and user feedback to identify areas for improvement. Track user behavior to see where they struggle and gather feedback to understand their pain points.
Short and Focused Onboarding: Keep the onboarding process short and focused on the most important tasks and features. Avoid overwhelming users with too much information at once; instead, introduce advanced features gradually as users become more familiar with the app. Incorporate a progress bar to visually represent the user’s progress, leveraging the Zeigarnik effect to motivate task completion. 86% of people say they’d be more likely to stay loyal to a business that invests in welcoming and educational user onboarding content.
Using these strategies and considering the user's perspective, product teams can create an effective, efficient, and engaging mobile app onboarding process that helps new users quickly realize the app's value.
Using customer feedback for onboarding
Customer feedback can be used to inform the onboarding process in several ways:
Identifying Areas of Confusion: Use feedback to pinpoint where users are getting stuck or confused. Provide additional support or guidance in these areas to help users overcome obstacles. In-app Microsurveys are great for this.
Prioritizing Features: Understand which features are most important to users and prioritize them in the onboarding process. Tailor the experience to highlight these features and show users how to benefit from them.
Refining the User Interface: Use feedback to refine the user interface and make it more intuitive. Small changes, such as improving button placement or simplifying navigation, can significantly enhance the user's experience.
Developing New Features: Identify specific user needs and pain points that your product does not currently address. Use this information to develop new features and functionality that meet these needs.
Continuous Iteration: Onboarding is a continuous process. Regularly collect and analyze feedback to make ongoing improvements. Use analytics to track the effectiveness of changes and ensure that the onboarding process evolves with user needs.
By using customer feedback to inform the onboarding process, product teams can create a more effective and engaging user experience that meets their users’ needs. This iterative approach ensures that the onboarding process remains relevant and valuable, helping users achieve their goals and become loyal advocates of your product.
Remember, it's a continuous process
User onboarding is not a one-time event, but rather a continuous process that requires ongoing effort and attention. It is essential to recognize that onboarding is an ongoing process that continues beyond the initial sign-up or purchase. By continuously refining and updating the onboarding process, you can ensure that users remain engaged and find ongoing value in your product. This approach not only helps retain users but also turns them into advocates for your product.
H2: Five expert-led user onboarding best practices
Onboarding best practices bridge the gap between theory and action. Instead of reinventing the wheel, these practices offer a structured approach to designing experiences that work.
Segmenting users based on user type can create more effective onboarding best practices by addressing the unique needs and interactions of different user groups.
Incorporating onboarding elements, such as tooltips and triggers, is essential for enhancing user experience and facilitating product adoption. These versatile tools help new users quickly understand and navigate the product, ultimately leading them to realize its value sooner. Onboarding design articles often highlight the importance of these strategies in creating effective and engaging onboarding processes.
1. Personalize your onboarding
Personalized onboarding makes users feel seen and understood. It tailors the onboarding process to someone’s needs, goals, or preferences instead of offering a generic experience.
To enhance user onboarding experiences, it is crucial to segment users based on their specific needs and roles, or user type. By understanding different user segments through surveys and product analytics, you can tailor the onboarding process to improve engagement and meet the unique objectives of each group. This dynamic approach is essential for accommodating a growing user base. In fact, 81% of customers now prefer companies that offer a personalized experience during onboarding.
Take the example of FullStory. During onboarding, they ask questions like where you work, your industry, and the websites where their tool will be installed. This information helps them customize the experience from the start, ensuring the setup process feels relevant and aligned with the user’s goals.
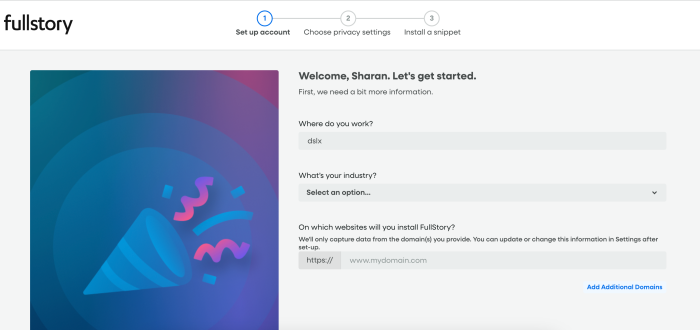
(Source)
Lumosity applies a similar technique. Before a user even enters an email address, they’re asked to answer a few questions. Lumosity creates a personalized training program, showing users exercises and games that apply specifically to what the user said they wanted to see.
2. Test and measure your onboarding success
Start by defining clear metrics to evaluate success from the user's perspective. Look for data points like:
Completion rates: Are users making it through your onboarding flow?
Time to first value: How quickly do users reach their “aha” moment?
Drop-off points: Where do users lose interest or get stuck?
Understanding where users drop off during the onboarding process is crucial. Use metrics and A/B testing to identify stages with high drop-off rates and implement in-app surveys to gather user feedback at critical points. User onboarding success can be measured by metrics such as activation rates and user engagement.
Once you have a baseline, test your onboarding flow. Use A/B testing to experiment with different formats, steps, or messaging. For example, test whether a tooltip or a product tour drives better engagement. Gather feedback through surveys or in-app prompts to understand user pain points. A high checklist completion rate correlates with user activation and suggests successful onboarding.
With user onboarding tools like Chameleon, you can easily track user interactions and engagement during onboarding. The dashboard provides actionable insights into user behavior, helping you identify bottlenecks and optimize flows in real time.
Plus, Chameleon’s in-app feedback tools let you collect user opinions, so your onboarding process stays user-focused and effective, ultimately helping to cultivate power users.

3. Focus on the fundamentals
One big mistake product teams make is trying to teach everything or hand-holding new users through every single obscure feature and aspect of the product. Don’t do this! Embrace self-discovery!
Users that are motivated will explore the product and figure out many things. Therefore it’s important to focus first on ensuring they understand the core value proposition to motivate them to explore. Considering the user's perspective is crucial in this process, as it helps tailor the onboarding experience to their specific needs and preferences.
For SaaS companies, structuring onboarding tasks effectively is crucial to enhance user experience. Collaborative efforts from product, engineering, and customer success teams can streamline the onboarding process and minimize the time spent on training new users.

Here’s how to apply these fundamentals effectively:
Break onboarding into stages: Users don’t need to learn everything at once. Start with essential actions—like account setup or completing a task. Gradually introduce advanced features as they become familiar with your product.
Make onboarding continuous: Onboarding shouldn’t stop after the first session. Use contextual prompts like tooltips or in-app messages to introduce new features when users are ready for them. For example, LinkedIn guides users to discover features like endorsements or groups only after they’ve built their profile.
Prioritize relevance: Avoid overwhelming users with irrelevant information. Tailor the onboarding experience based on their behavior or goals to keep it meaningful and engaging.
Focus on retention and growth: Retaining users means constantly showing them more value. Highlight how premium features or upgrades can enhance their experience. Tools like modals or interactive tours are great for educating users about features they might have missed. (Source)
“If a customer is stuck, getting them unstuck in a way that not only satisfies them, but makes them excited to keep using the product is one of the most powerful things you can do to increase retention.”
4. Create a framework for reiteration
One of the hardest aspects of effective user onboarding is the framework you implement to guarantee consistency and continuous improvements by significantly enhancing user engagement and success. Considering the user's perspective is vital in developing this framework, as it ensures that the onboarding process is intuitive and engaging, addressing the specific needs and preferences of users.
This should consist of:
who (responsible people)
when (cadence of experiments)
why (clear metrics and goals)
where (channels used)
what (content)
how (design style)
For more sophisticated teams this can contain more specific guidelines on how and how much to target each group of users.

User onboarding should grow with your product. A flexible framework for reiteration ensures your onboarding stays as dynamic as your product. Resource centers play a crucial role in this by providing self-service support materials directly within the application, allowing users to resolve issues on demand without leaving the app.
Here’s how to keep it evolving:
Update onboarding with every product change: Added a new feature? Launched a redesign? Make sure your onboarding reflects those updates. Use contextual nudges, like modals or tooltips, to introduce users to what’s new without overwhelming them.
Let user data lead the way: Use Chameleon to track where users engage—or get stuck. If everyone’s abandoning a flow halfway, that’s your cue to revisit and tweak it.
Test like a scientist: Don’t guess what works—test it. A/B test onboarding flows or messages to see what gets the best results. Does a tooltip get users clicking faster than a walkthrough? Find out and optimize accordingly.
Ask users what they need: Add in-app surveys or quick feedback forms to learn where users want more help. Then, act on what they tell you.
Build with flexibility in mind: Products change and onboarding should too. Use modular designs that let you swap in new steps or remove irrelevant ones without breaking the entire flow.
5. Use a platform to build in-product guidance
Creating in-product guidance can be complex—but it doesn’t have to be. Platforms like Chameleon make it easy to build intuitive user onboarding flows and interactive experiences right inside your product. By considering the user's perspective, Chameleon allows you to deploy tooltips, modals, product tours, and hotspots that guide users step-by-step, so they discover the features that matter most.
Custom dashboards are crucial for tracking user engagement. Features like Event Explorer enable users to create tailored visualizations of specific user segments, enhancing the understanding of product interaction among different groups. One user expressed satisfaction with how these features streamline the task documentation process.
Want to see it in action? Try the interactive demo below!
Propel product adoption with smooth user onboarding
User onboarding is about approaching your product with a philosophy that the more users learn and discover, the more value they will get from a product. A great onboarding strategy ensures users feel supported not just at the start but throughout their journey with your product. Considering the user's perspective is crucial in propelling product adoption, as it ensures the onboarding process is intuitive and engaging, addressing the specific needs and preferences of users.
With Chameleon, you can create onboarding experiences that adapt as your product evolves. From building product tours tailored to specific user needs to providing contextual guidance that keeps users engaged, Chameleon makes it easy to design flows that drive retention and growth.
If you’d like to learn what product tours you should be building based on your goals, our product specialists are here to help. Book a demo today or start exploring Chameleon for free to see how you can transform your onboarding process into a tool for lasting success.