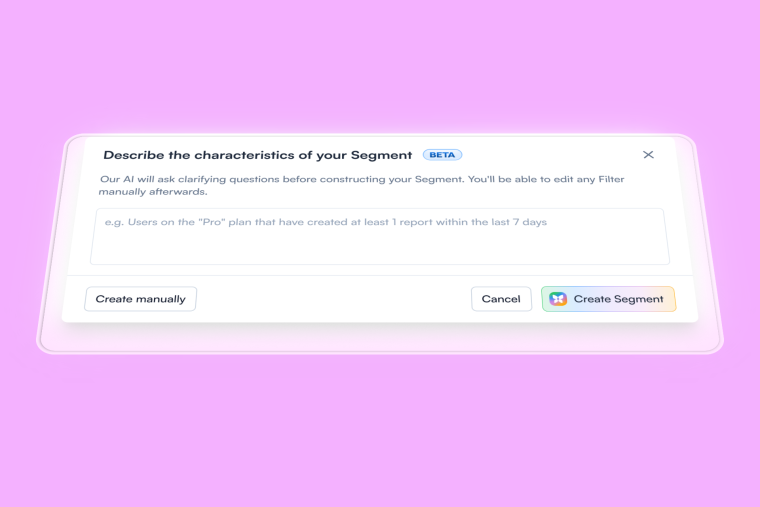
Your onboarding flow has layers upon layers of tours, tooltips, and emails. Some are performing well. Others? You're not entirely sure they're even still relevant. And that "welcome tour" you built two years ago that shows off every feature? Yeah, users are dismissing that faster than you can say "skip intro."
The traditional approach to fixing this involves endless spreadsheet analysis, watching session recordings until your eyes glaze over, and having the same "what's our aha moment?" debate with your team for the third time this quarter.
AI can actually help you cut through all that noise. Not in a "let's automate everything and hope for the best" way, but in a "let's use this to surface insights we'd never spot manually" kind of way.
We recently hosted a webinar where Pulkit Agrawal, Chameleon's CEO, shared 10 practical approaches for leveraging AI to enhance activation and conversion. These aren't theoretical plays. They are things you can test this week with tools you probably already have access to. Let's dive in.
The TL;DR of using AI in user onboarding
-
Stop guessing at user segments. Export behavior data and let AI identify patterns that separate successful users from churners.
-
Find your real aha moments. Use AI to analyze retention data and discover which early actions correlate most strongly with long-term success, then build onboarding around those actions.
-
Clean up your onboarding debt. AI can audit all your tours, tooltips, and emails to flag overlapping content, outdated references, and low-engagement experiences.
-
Test smarter re-engagement angles. Generate three different psychological approaches for each drop-off point instead of generic "finish setup" emails.
-
Analyze friction without watching endless session recordings. Upload screenshots of your onboarding flow and get feedback on confusing elements and unclear CTAs.
-
Chameleon users get AI built in. Generate copy from help docs, create AB test variants automatically, turn Loom recordings into interactive demos, and use Ranger Agent to clean up workspace clutter (Copilot launching soon).
1. Segment Discovery Through Behavioral Pattern Mining
What AI does: Identifies hidden behavioral patterns that differentiate successful users from those who churn, going way beyond basic demographic segmentation.
How to do it:
Export user data from your analytics tool (Amplitude, Mixpanel, whatever you use) as a CSV. You'll want columns for user_id, signup_date, whether they activated (yes/no), whether they churned (yes/no), and then 10-15 key actions like completed_profile, invited_teammate, created_first_project.
Upload this to ChatGPT or Claude and prompt it:
Analyze this user behavior data. Identify 3-5 non-obvious behavioral segments that differentiate activated from churned users. Look for sequences (e.g., 'users who did X before Y') and combinations that traditional demographic segments would miss.
What you get:
Insights like "Early Collaborators: Users who invite a teammate within first 3 days before completing their own profile have 78% activation vs. 34% baseline. Prioritize team setup over individual feature tours."
You might be using something like demographics, like we've got people who are large companies and small companies or marketers and designers. You might be doing high level variations of onboarding, but you can also get to the behavioural understanding.
These behavioral segments often reveal your actual "magic number" moments, the ones that correlate most strongly with success.
2. Time-to-Value Optimization
What AI does: Analyzes retention data to identify which early actions correlate most strongly with long-term success, so you know exactly which "aha moment" to drive users toward.
How to do it:
Create a CSV with user_id, signup_date, retained_30_days (yes/no), and then timestamps for your first 15-20 possible actions (first_project_created_day, first_invite_sent_day, etc.). The values should be the number of days since signup when they completed each action, or null if they never did.
Upload to ChatGPT's Advanced Data Analysis and ask it to:
Analyze correlation between early actions (within first 7 days) and 30-day retention. Rank actions by correlation strength with retention, typical timing, and completion rate. Then suggest an optimal activation sequence.
What you get:
Clear direction like "Users who create a project (Day 1, 67% completion) then invite teammate (Day 2) have 2.3x retention vs. users who view report first. Recommended sequence: Project creation → Team invite → Report view."
This isn't about causation (yet), but correlation is a solid starting point for understanding what successful users actually do.
3. Feature Sequencing Logic
What AI does: Determines the natural order in which successful users adopt features, so you can build progressive disclosure instead of overwhelming everyone with everything at once.
How to do it:
Export feature adoption data for retained users only. Each row represents one user, with columns showing "days until first use" for each feature (or null if they never used it).
Feed this into ChatGPT with the prompt:
Analyze the sequence in which successful users adopted features. Identify which features are foundation features, common adoption sequences, and prerequisite patterns. Recommend a 3-tier progressive disclosure: Week 1 features, Week 2 features, Month 1 features.
What you get:
A clear hierarchy showing that Feature Y is rarely adopted unless users have already engaged with Feature X. This is gold for targeting your in-app experiences.
When somebody uses X feature and then they use Y feature, that's really valuable because then when you're ever signposting Y feature or you want to promote Y feature, you target it to people who've done X feature, and that way you can get your in-app experiences much more targeted to the right users who might likely care about feature Y.
Stop promoting features broadly and start targeting them to users who are actually ready for them.
4. Onboarding Debt Audit
What AI does: Scans all your onboarding experiences and flags overlapping content, low engagement, outdated references, and abandoned experiments.
How to do it:
Export all active onboarding experiences from your tool (Chameleon, Pendo, etc.) as a CSV with: experience name, type, created date, last edited, shown count (30 days), completion rate, target audience, and a content snippet.
Upload to ChatGPT and ask it to:
Audit these onboarding experiences for technical debt. Flag HIGH PRIORITY issues like overlapping content, low engagement, and likely outdated references. Then prioritize the top 5 experiences to deprecate or fix first.
What you get:
A prioritized list of what's cluttering your workspace and confusing your users. Maybe two tours explain the same feature. Maybe something references a "new feature" from 2022. Maybe an abandoned experiment is still showing to users.
Quick plug: We've built this directly into Chameleon through our Ranger agent, which automatically audits your workspace and suggests cleanup actions. But you can absolutely do this manually with any tool you're using.
5. Onboarding Friction Heatmap Analysis
What AI does: Analyzes screenshots of your onboarding flow to identify specific UI elements that would confuse new users, going beyond what drop-off metrics can tell you.
How to do it:
Take screenshots of each onboarding step (5-10 images) and upload them to ChatGPT-4 with Vision or Claude. Prompt it:
You're a UX researcher analyzing an onboarding flow. For each screenshot: identify elements that would confuse a new user, spot missing context or unclear CTAs, note information overload, and suggest one specific fix per screen. Be critical.
What you get:
Specific feedback like "The CTA on screen 3 says 'Continue' but doesn't indicate what comes next. The form on screen 5 has 8 fields when users typically expect 3-4 at this stage."
I sometimes notice in onboarding, people are highlighting things that don't need highlighting. They're really obvious and easy to understand, but people are highlighting them anyway because they think that's an important action, but that's not the problem.
Bonus: Include a screenshot of a competitor's equivalent step and ask "Compare to this competitor approach. What are they doing better?"
6. Competitive Onboarding Intelligence
What AI does: Extracts patterns from competitor onboarding flows to identify market standards, differentiators, and opportunities you're missing.
How to do it:
Use Loom to record 5 competitor onboarding flows (3-5 minutes each). Talk through your thoughts as you record. Say things like "I like this CTA copy because it tells me what's coming next" or "This step is confusing, I'm not sure what to do." Your commentary becomes rich context in the transcript.
Get the transcripts (Loom has AI transcript features), combine them into one document, and prompt:
These are transcripts from 5 competitor onboarding flows. Identify: universal patterns (what do ALL of them do?), differentiators (what does only 1-2 do?), gaps (what is NO ONE doing well?), and our opportunity.
What you get:
Insights into what's table stakes vs. what could be your differentiator. Maybe everyone has a team invite step but no one's doing it particularly well. That's your opportunity.
7. Help Content Gap Analysis
What AI does: Clusters support tickets to identify common confusion points and maps them to specific onboarding stages, so you know exactly what preventive content to create.
How to do it:
Export support tickets from the last 60 days for users within their first 14 days after signup. Include user_signup_date, ticket_date, days_since_signup, ticket_subject, and ticket_body.
Upload to ChatGPT and prompt:
Analyze these early-user support tickets. Group questions into clusters by theme. For each cluster: identify the common question pattern, typical point in onboarding, suggested preventive content type (tooltip, tour step, help doc, email), and draft title.
What you get:
Actionable insights like "Cluster: API authentication confusion. Appears at Days 2-5. 23 tickets. Suggested fix: Inline tooltip on API keys page. Title: 'Where to find your API credentials and test your first call.'"
Help docs are so key because they are going to be the basis of a lot of agentic workflows. It's really important to invest in your help content to make sure that any agents, yours, support tickets, support agents, are effective
The channel is shifting. Users aren't navigating help indexes anymore. They're asking agents questions. Those agents need comprehensive, well-structured content to pull from.
8. Alternative Re-engagement Approaches
What AI does: Generates context-specific re-engagement emails based on exactly where users dropped off, with different psychological angles to test.
How to do it:
Map your key activation steps with drop-off rates. For each major drop-off point, prompt:
User abandoned onboarding at [Step 3: Connect integration]. They completed email verification and profile but haven't connected an integration. Generate 3 different re-engagement email angles: Friction-reducer (assumes technical barrier), Value-reinforcer (assumes they forgot why this matters), Alternative-path (offers workaround or simpler option).
What you get:
Three distinct approaches to test instead of one generic "finish setup" email. The friction-reducer might say "Integration taking longer than expected? Here's how to connect in under 2 minutes." The value-reinforcer reminds them why this step unlocks specific outcomes. The alternative-path offers a different way to get value.
I think the benefit of thinking about these through these categories is it might really change some of your approach, which might be by default friction reduction. It might be missing the value. Or maybe it's very value forward, but it's missing the how do you actually do it.
9. Persona-Based Messaging
What AI does: Instantly generates persona-specific variants of your onboarding copy for testing, going beyond basic demographic splits.
How to do it:
Copy your current onboarding message and prompt:
Rewrite this for 3 personas: Technical founder (direct, assumes competence, focuses on implementation), VP Product (strategic, ROI-focused, outcome-oriented), and Non-technical team member (supportive, step-by-step, ease of use focused).
What you get:
Three genuinely different versions optimized for different mindsets. But don't just think about role-based personas. Consider motivation-based personas.
One other axis to play with in terms of persona is motivation. I often see with products that there are at least two versions of the motivation axis. One is high motivation and intent, meaning they're ready to purchase or they're actively evaluating. That persona is very different from the low motivation kind of discovery level where someone may have come across this product through some Twitter feed.
High-intent users need to get to value quickly. Low-intent users need more coaching and value demonstration. Same product, completely different onboarding approach.
10. Localization Beyond Translation
What AI does: Provides cultural UX guidance beyond just translating text, accounting for different interaction patterns and expectations across markets.
How to do it:
Screenshot your current onboarding flow (5-8 screens) and upload to ChatGPT or Claude. Prompt:
I'm localizing this for [German/Japanese/Brazilian] users. Beyond translating text, what UX adaptations should I make? Consider form field expectations, visual density, trust signals, and interaction patterns.
What you get:
Specific guidance like "German users expect more detailed form validation messages and typically prefer linear flows over exploratory navigation" or "Japanese users respond better to visual progress indicators and expect more formal tone in instructional content."
Advanced version: Include screenshots of successful local products in that market and ask what patterns they share that differ from US norms.
Bonus: Ways to Use AI in Chameleon
If you're already using Chameleon (or thinking about it), AI is baked directly into the product:
Generate copy from existing documents: Link to a help article and Chameleon will summarize it into the most valuable piece for a tooltip or tour step.
Create AI variants for AB tests: Got one version of an announcement? Chameleon can generate an alternative version automatically, making it stupid easy to test variations.
Summarize Microsurvey responses: Run a feedback survey and get all the comments automatically summarized into themes so you can actually act on them.
Record a video to generate an Interactive Demo: Talk through a feature or workflow in a Loom-style recording and convert it into an interactive, clickable demo that people can experience without needing product access.
Ranger Agent cleans up your workspace: This AI agent looks for experiences that haven't been seen recently, improves naming conventions, removes clutter like unused segments or themes, and identifies inactive teammates taking up seats. It suggests actions in your governance hub and you decide what to act on.
For some of our customers that have hundreds of experiences, large teams, multiple groups of people using Chameleon, it's really powerful to help reduce clutter, keep your workspace clean and really easy to use.
Coming soon: Chameleon's Copilot is a broad-based AI assistant trained on Chameleon best practices. It can analyze existing experiences, suggest and make improvements, create entire campaigns to meet specific goals, troubleshoot issues, and help you level up on best practices. It does its own research and constructs experiences for you, which you can then tweak as needed.
🤖 Check out Chameleon's AI features here.
The Bottom Line
None of these approaches require you to be an AI expert or rebuild your entire onboarding stack. They're practical ways to surface insights and patterns that would take weeks to uncover manually.
The goal isn't to automate everything. It's to use AI where it actually makes sense: processing large amounts of data, spotting patterns, generating variations, and giving you a starting point that's way better than a blank page.
Start with one. Pick the approach that addresses your biggest current pain point. Export some data, write a prompt, see what you get.
Your onboarding flow will thank you. So will your users.
Book a demo to discover AI-first user onboarding
So you can get back to orchestrating product adoption